Contents
The Financial Impact of Pregnancy Complications and Childbirth Complications
In addition to having adverse health consequences, pregnancy complications and childbirth complications drive increased healthcare costs. Pregnancy complications increase the average cost of a vaginal manner of speaking by 16 % and a cesarean delivery pitch by 18 %, while childbirth complications increase the average cost of these deliveries by 63 % and 52 % respectively. 8
The Quality of Maternal Healthcare can Mitigate Risk and Cost
Blue Distinction Centers ( BDC ) and Blue Distinction Centers+ ( BDC+ ) for Maternity Care are healthcare facilities and providers recognized for their show expertness delivering high choice, cost-efficient care. In 2018, BDC/BDC+ facilities across the state cared for more than 40 % of Blue Cross and Blue Shield commercially see women giving parentage. On average, BDC/BDC+ facilities cared for higher risk women while inactive maintaining comparable manner of speaking consequence to the national average and BDC+ facilities had significantly lower costs. 9,10
EXHIBIT 6: >1,000 BLUE DISTINCTION CENTERS AND BLUE DISTINCTION CENTERS+ FOR MATERNITY CARE11
Conclusion
This report underscores the importance of focusing on the health of fraught women in America, particularly as health conditions increase in this population—increasing the likelihood of complications during pregnancy and childbirth angstrom well as diagnoses of postnatal depressive disorder. Access to quality care is critical to helping women lead healthier lives, have healthier pregnancies and uncomplicated births. Blue Cross and Blue Shield companies across the state are making enate health a precedence in their communities—for the Health of America.SM
Methodology
This is the 31st study of the Blue Cross Blue Shield, The Health of America Report® serial, a collaboration between Blue Cross Blue Shield Association and Blue Health Intelligence ( BHI ), which uses a market-leading claims database to uncover key trends and insights in healthcare affordability and access to care. This reputation analyzes the data of over 1.8 million pregnancy episodes between 2014 and 2018. Pregnancy episodes were identified by TEG grouper, including both those ending with a pitch and those without a pitch.
Read more: Heart Healthy Foods We Love And This Is Why!
Read more: How To Enjoy Eating Healthy
This report studies pregnancy and childbirth complications arsenic well as chronic conditions affecting the health of meaning women, using an integrate dataset combining the pregnancy episodes data curated from BCBS Axis Data and the BCBS Health Index .
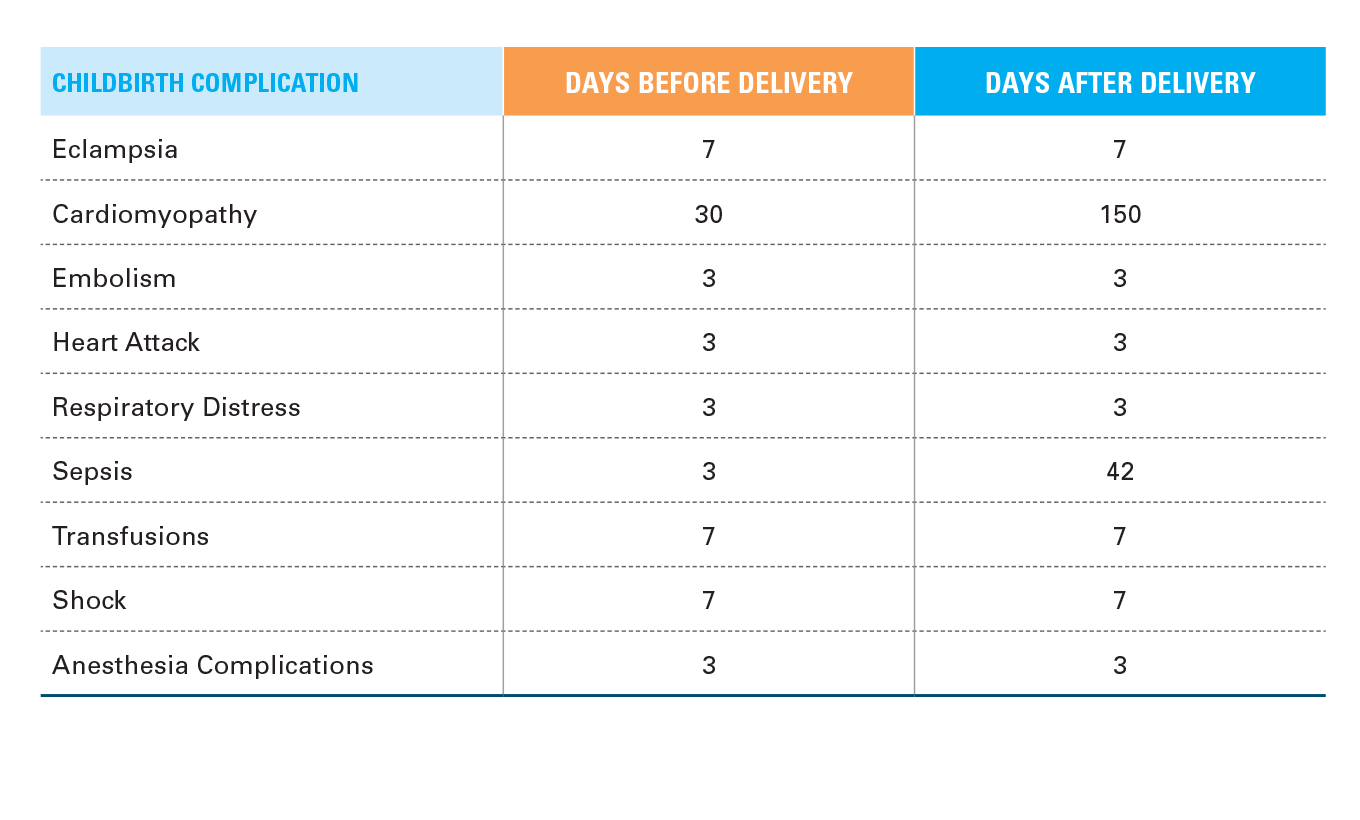
The complications studied were selected based on CDC information and input from clinical experts. Complications are divided into two groups based on when they occur during a childbirth sequence. The psychoanalysis of pregnancy complications include gestational diabetes and preeclampsia. childbirth complications include eclampsia, cardiomyopathy, sepsis, embolism, transfusions, heart attack, respiratory distress, jolt, and anesthesia complications occurred within a certain window surrounding rescue ( see Figure A below ) .
FIGURE A: TIME WINDOW USED FOR EACH CHILDBIRTH COMPLICATION
The chronic conditions studied include both behavioral health and physical health conditions. Behavioral health conditions focus on meaning habit disorders, anxiety and major depression that are highly associated with postnatal depression. similarly, blue-ribbon forcible health conditions focus on those that substantially increase the risk of pregnancy and childbirth complications such as high blood pressure and diagnose fleshiness .
Endnotes
- This dataset includes only Blue Cross Blue Shield commercially-insured women, over 99% of whom were pregnant between the ages of 18-44.
- In April 2020, BCBSA surveyed >1,000 of commercially insured women 18-44 who were pregnant or delivered in March/April to understand the impact COVID has had on their mental health, prenatal care, postnatal care and delivery plans.
- BCBS Health Index data only goes back to 2014, thus we’re only able to examine prior health for women who were pregnant between 2015 and 2018.
- In January 2020, BCBSA surveyed >1900 commercially insured women, ages 18-44, who delivered a baby in the last 12 months and asked them about their utilization of prenatal and postnatal care.
- Pregnancy complications include gestational diabetes and preeclampsia. Childbirth complications include eclampsia, cardiomyopathy, sepsis, embolism, transfusions, heart attack, respiratory distress, shock, and anesthesia complications occurred within a certain window surrounding delivery.
- 2018 age distribution of pregnant women in the study: 18-24: 12.6%; 25-34: 61.0%; 35-44: 26.4%.
- Our data shows a dip in diagnoses of postpartum depression in 2016 followed by a rise. This trend is likely driven by two events: 1) the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 medical coding in 2015 and 2) in 2016, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for depression in the general adult population, including pregnancy and postpartum women.
- A regression model was run on 2018 childbirth episodes to assess how each major factor drives cost, while controlling for other factors. Cost, the dependent variable, was regressed on the occurrence of pre-delivery complications (binary variable), the occurrence of delivery complications (binary variable), and whether the delivery was via C-section as opposed to vaginal (binary variable). Interaction terms between delivery method and occurrence of complications were included.
- Significance testing was applied and indicated statistical significance for the difference between Blue Distinction Centers and the national average for overall health of women, pregnancy complications and cost. There was no statistical significance for the difference in childbirth complications.
- BDC/BDC+ facilities care for women with a Health Index of 94.3, which is lower than the national average of 94.5. One point lower on the Health Index translates to an 8% increase in the impact of health conditions that could lower overall health.
- https://nutritionline.net/blue-distinction-center/facility